Understanding Genital Warts
What Are Genital Warts?
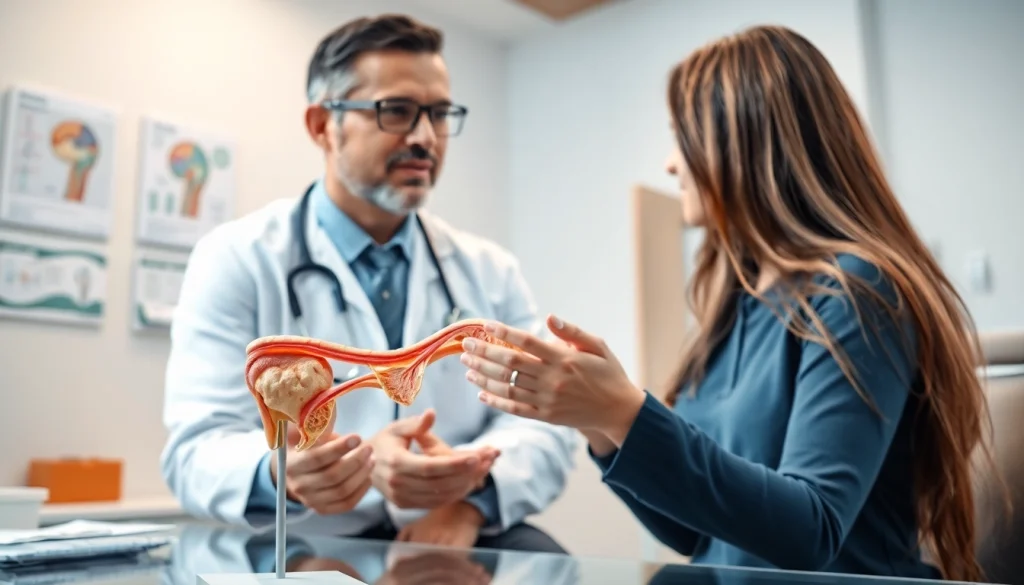
Genital warts are small, fleshy growths that appear on or around the genital area. They are a common symptom of an infection by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which has over 100 strains, some of which are regarded as low risk and can lead to genital warts, while others are classified as high risk and can result in cancers. Although genital warts can appear in various shapes and sizes, they are typically soft to the touch and may resemble cauliflower or small bumps. They can be white, pink, or flesh-colored and often occur in clusters.
Causes of Genital Warts
The main cause of genital warts is the transmission of HPV through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. While frequently associated with sexual intercourse, it is important to note that skin contact during close physical interactions can also transmit the virus. Factors such as a weakened immune system, the number of sexual partners, and engaging in unprotected sex can increase the risk of contracting HPV and developing genital warts.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Treatment
Symptoms of genital warts can vary significantly among individuals. Some may experience noticeable growths, while others may display no visible signs. Common symptoms include:
- Small, raised or flat growths on the genital area
- Itching or discomfort around the affected areas
- Bleeding during sexual intercourse
- Changes in the appearance of the skin around the genitals
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and to discuss the Best genital warts treatment options available.
Treatment Options for Genital Warts
Topical Treatments for Best genital warts treatment
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against genital warts, especially for those with mild cases. These treatments can be prescribed by a healthcare professional and are applied directly to the warts. Common topical options include:
- Imiquimod: A cream that boosts the immune response to fight HPV. It is typically applied three times a week at bedtime.
- Podophyllotoxin: A plant-based solution that is used twice a week. It works by destroying wart tissue.
- Trichloroacetic acid (TCA): A chemical treatment applied by a healthcare provider that can burn away warts.
Effectiveness can vary, with some people experiencing complete resolution of their warts, while others may require multiple cycles of treatment.
Procedural Interventions Explained
In cases where topical treatments are ineffective or unsuitable, procedural interventions may be recommended. These include:
- Cryotherapy: Involves freezing the warts with liquid nitrogen, which causes the tissue to fall off.
- Electrosurgery: Uses electric current to burn off warts.
- Laser therapy: A high-energy laser beam is used to destroy warts.
- Surgical excision: The warts can be surgically removed, which might be necessary for larger growths.
Each method has its advantages and potential side effects, and treatment should be tailored to the individual’s specific condition.
Choosing the Right Treatment Plan
Deciding on the best treatment plan for genital warts involves considering various factors, including the number and size of warts, patient preference, and any medical history that may influence treatment choice. It’s essential to have an open dialogue with a healthcare provider who can guide patients through the options and expected outcomes. Furthermore, some individuals may find success using a combination of topical and procedural treatments.
Preventing Genital Warts
Vaccination and Safety Practices
Prevention of genital warts begins with protecting oneself against HPV. The HPV vaccine is highly effective in preventing the types of HPV that cause most genital warts. It is recommended for preteens and can be beneficial even for those in their twenties. In addition to vaccination, practicing safe sex, such as using condoms and being selective about sexual partners, can significantly reduce the risk of HPV transmission.
Regular Health Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are vital for maintaining sexual and reproductive health. Routine screenings can help identify potential issues early, including the presence of HPV or genital warts, allowing for timely intervention. Engaging in open conversations with healthcare providers about sexual health can provide guidance and reassurance.
Open Communication with Partners
Communication is a cornerstone of healthy sexual relationships. Discussing sexual health and histories with partners can help mitigate risks for both individuals. It is critical to inform partners if you have been diagnosed with HPV or have any concerns regarding genital warts, as this allows for informed decision-making regarding sexual practices and health management.
Managing Emotional Impact
Addressing Stigmas and Misconceptions
The diagnosis of genital warts can be emotionally challenging, often linked with feelings of shame or embarrassment. It is important for individuals to recognize that HPV is very common and that genital warts are a manageable health concern. Educating oneself about the condition can help dismantle harmful stigmas and foster a supportive environment for those affected.
Finding Support Networks
Finding support through friends, family, or dedicated support groups can provide comfort during this time. Shared stories and experiences within these support networks can help individuals feel less isolated and encourage an open dialogue about sexual health and experiences with HPV.
Professional Counseling Options
Cognitive behavioral therapy or counseling can be beneficial for those struggling with emotional distress stemming from genital warts or the associated HPV diagnosis. Professional therapists can assist individuals in developing coping strategies and addressing anxiety, self-esteem issues, or relationship challenges that may arise from the diagnosis.
Long-term Outlook and Follow-up Care
Monitoring Treatment Effectiveness
After initiating treatment for genital warts, it is crucial to monitor the effectiveness of the chosen plan. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider can help evaluate treatment success and determine the need for further intervention. This ongoing assessment is critical for preventing recurrence and managing any potential long-term complications.
Long-term Health Considerations
Even after treatment, it is essential to remain vigilant about sexual health and monitor for any new symptoms. The variability of HPV means that individuals should continue to check for changes in their bodies, attend regular medical check-ups, and maintain healthy practices to promote overall well-being.
When to Seek Further Medical Advice
In certain situations, individuals should seek further medical help, including:
- If warts continue to persist after treatment
- Experiencing unusually severe pain or discomfort
- Noticing changes in the appearance of the skin around the genitals
- Having questions or concerns about HPV or genital warts
Timely medical consultations are crucial for managing health concerns effectively and reducing anxiety related to the condition.