Understanding Informatics in Healthcare
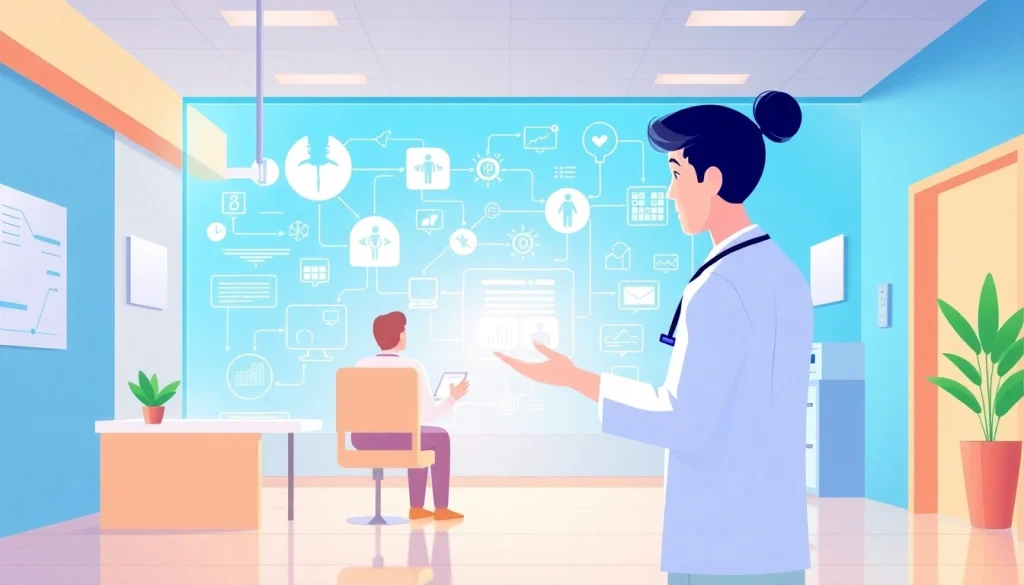
Informatics plays a pivotal role in revolutionizing healthcare, utilizing data and technology to improve the delivery of care and enhance patient outcomes. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the importance of informatics only deepens, merging the fields of data science, communication technology, and clinical practice to create efficient systems. Organizations are increasingly turning to platforms like informaticsview.com to explore the latest developments and insights in this transformative field.
Definition and Scope of Informatics
Informatics can be broadly defined as the science of how to use data, information, and knowledge to improve human health and the delivery of healthcare services. It encompasses a variety of disciplines, including health informatics, biomedical informatics, and nursing informatics. This multidisciplinary focus allows informatics professionals to address various healthcare challenges, create innovative solutions, and facilitate communication among healthcare providers and patients.
Key Components of Informatics Systems
Informatics systems consist of several integral components:
- Data Collection: Involves gathering data from various sources, such as electronic health records (EHRs), laboratory systems, and clinical databases.
- Data Management: Refers to the organization, storage, and retrieval of data, ensuring it is easily accessible and secure.
- Analytics: The analysis of data to derive insights and inform clinical decision-making, enabling healthcare providers to offer personalized patient care.
- Communication: Facilitates the seamless exchange of information among healthcare professionals, patients, and systems to enhance collaboration and coordination.
Impact of Informatics on Patient Care
The integration of informatics into healthcare has had a profound impact on patient care, leading to improved clinical outcomes and enhanced efficiency. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Patient Safety: Informatics systems identify potential errors in treatment plans or medication administration, thereby reducing adverse events.
- Personalized Care: By analyzing patient data, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to individual needs, improving health outcomes.
- Increased Accessibility: Telehealth services enabled by informatics allow patients to access care remotely, breaking down geographical barriers.
- Efficient Workflow: Automation of routine tasks, such as documentation, helps streamline operations and allows healthcare providers to focus more on patient interaction.
Essential Tools and Technologies in Informatics
Electronic Health Records (EHR) and Their Importance
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are among the most significant innovations in healthcare informatics. EHRs consolidate patient information, including medical history, medications, allergies, and treatment plans, into a single digital format that can be accessed by authorized healthcare providers. The benefits of EHRs include:
- Improved Coordination: Multiple providers can access the same patient data, promoting collaborative care.
- Enhanced Quality of Care: EHRs provide clinical decision support tools, reminders for preventive care, and alerts for potential drug interactions.
- Data Analytics: EHR systems can generate reports and analytics that inform population health management and quality improvement initiatives.
Clinical Decision Support Systems Overview
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) are advanced tools that analyze patient data and provide evidence-based recommendations and alerts to healthcare providers. These systems can help clinicians make better diagnostic and treatment decisions, thereby enhancing patient safety and outcomes. Key features include:
- Knowledge Databases: CDSS utilize vast databases that incorporate the latest clinical guidelines and research findings.
- Real-Time Alerts: They offer notifications for critical lab results, medication interactions, and contraindications, aiding in timely interventions.
- Patient-Centric Recommendations: CDSS provide personalized suggestions based on individual patient characteristics and preferences.
Wearable Technology and Patient Monitoring
Wearable technology, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, is becoming increasingly prevalent in healthcare informatics. These devices enable continuous patient monitoring outside of clinical settings, allowing for:
- Real-Time Health Data: Wearable devices collect vital signs, physical activity, and other health metrics, providing continuous insights into a patient’s condition.
- Engagement and Empowerment: Patients are encouraged to take charge of their health through self-monitoring and informed decision-making.
- Remote Monitoring: Healthcare providers can monitor patients remotely, facilitating proactive interventions when necessary.
Implementing Informatics Solutions: Best Practices
Assessing Needs and Selecting the Right Tools
Before implementing informatics solutions, healthcare organizations must conduct a thorough needs assessment. This involves analyzing current processes, identifying pain points, and determining specific goals. A successful transition involves:
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involve all relevant stakeholders, including clinicians, IT professionals, and administrative staff, to gather diverse perspectives and objectives.
- Technology Evaluation: Research and evaluate various tools and technologies, considering factors such as interoperability, ease of use, and vendor support.
- Budget Considerations: Allocate budget and resources wisely, examining the return on investment (ROI) of potential informatics solutions.
Training Staff for Effective Utilization
Successful implementation relies heavily on the training and support provided to staff members. Best practices for training include:
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Develop targeted training sessions tailored to different user roles, ensuring competence in system usage.
- Ongoing Support: Establish a support system for users post-implementation, including help desks and access to tutorials.
- Cultural Change Management: Foster a culture that embraces change and innovation, encouraging staff to adapt to new technologies.
Measuring Outcomes and Impact Analysis
Post-implementation, organizations must measure the effectiveness of informatics solutions. Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) is crucial to evaluate success, which may include:
- Patient Outcomes: Analyze improvements in patient satisfaction, safety metrics, and clinical outcomes.
- Efficiency Metrics: Assess changes in workflow efficiency, including reduced time spent on administrative tasks and improved clinical workflows.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Monitor the financial impact of implemented solutions, aiming to demonstrate cost savings and a favorable ROI.
Common Challenges in Health Informatics
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Data privacy and security remain significant issues within health informatics, as sensitive patient information is often stored in digital formats. Challenges include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Organizations must adhere to regulations such as HIPAA to protect patient data and ensure confidentiality.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Healthcare data breaches can have severe consequences, making it essential to implement robust security measures.
- Employee Training: Regular training programs on data handling and cybersecurity best practices are crucial to minimize risks.
Interoperability between Systems
Interoperability, or the ability of different healthcare systems to communicate and exchange data effectively, poses a ongoing challenge. Key issues include:
- Lack of Standardization: Various systems often use different data formats, making integration challenging.
- Vendor Lock-In: Organizations may be restricted by their vendor’s technology, hindering the seamless exchange of information.
- Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of data across different systems is critical for effective interoperability.
Resistance to Change in Healthcare Environments
Even with the clear benefits of informatics, resistance to change among healthcare professionals persists. Strategies to overcome this include:
- Inclusive Decision-Making: Involve end-users in the selection and implementation process to foster buy-in and understanding.
- Highlighting Benefits: Emphasize how new systems will alleviate pain points and improve their work experience.
- Phased Implementations: Gradually introduce new technologies, allowing users to adapt more easily over time.
Future Trends in Healthcare Informatics
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are set to redefine the healthcare informatics landscape. These technologies can analyze vast datasets to uncover patterns and support clinical decision-making. Key applications include:
- Predictive Analytics: AI can predict patient outcomes based on historical data, enabling preventive measures and personalized treatment.
- Natural Language Processing: This technology allows for improved data entry and information retrieval from unstructured data, such as clinical notes.
- Automated Diagnostics: AI algorithms can assist in diagnosing conditions by analyzing medical images and lab results.
Telemedicine Expansion and Its Benefits
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, and its benefits continue to resonate within the healthcare sector:
- Increased Access to Care: Patients in remote areas can consult healthcare providers without traveling long distances.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: By minimizing the need for in-person visits, telemedicine can lower costs for both patients and healthcare systems.
- Continued Monitoring: Chronic disease management is enhanced through regular virtual check-ins and remote monitoring of health conditions.
Data Analytics for Improved Decision Making
Data analytics is becoming an indispensable facet of healthcare informatics. By leveraging large datasets, healthcare organizations can improve decision-making processes:
- Population Health Management: Analytics enable healthcare systems to identify at-risk populations and develop targeted intervention strategies.
- Quality Improvement Initiatives: Data analysis drives initiatives that enhance patient care quality, safety, and operational efficiency.
- Resource Allocation: Intelligent data analytics informs resource allocation, allowing organizations to optimize staff and equipment deployment.