Introduction to Landguard Raised Beds
For gardening enthusiasts and novices alike, transforming outdoor spaces into flourishing green landscapes can be both a rewarding and fulfilling endeavor. Among the many tools and techniques available to enhance horticultural efforts, landguard raised beds stand out as an effective solution for maximizing space, improving soil conditions, and simplifying garden maintenance. This article delves deep into what makes these raised beds exceptional, their design options, installation processes, and best practices for ensuring a thriving garden.
What Are Landguard Raised Beds?
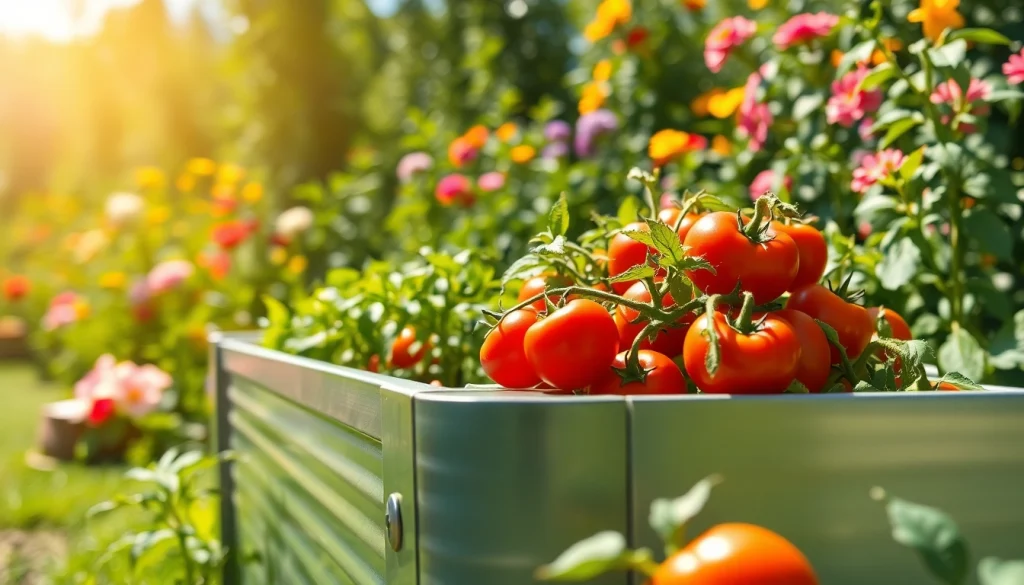
Landguard raised beds are specially designed planting structures that elevate the gardening area above ground level. Made from durable materials and available in various shapes and sizes, these garden beds facilitate better drainage, soil quality, and accessibility. They offer a controlled environment for plants, allowing for the cultivation of vegetables, herbs, and flowers while minimizing the interference from pests and weeds.
Key Features of Landguard Raised Beds
Several features make landguard raised beds attractive to garden enthusiasts. Here are some defining characteristics:
- Materials: Typically constructed from weather-resistant materials such as galvanized steel or treated wood, ensuring longevity and durability.
- Variety of Sizes: Available in different dimensions to suit various planting needs and space constraints.
- Customizable Designs: With options for colors and styles, these beds can blend seamlessly into existing landscapes, enhancing aesthetic appeal.
- Easy Assembly: Most units come with clear instructions and require basic tools for quick setup, making them accessible even for beginners.
Benefits of Using Raised Beds in Your Garden
The advantages of incorporating landguard raised beds into your garden are numerous. Here are some significant benefits:
- Improved Accessibility: Raised beds reduce strain on the back and knees, making gardening easier for individuals of all ages and abilities.
- Enhanced Soil Control: Gardeners can create a tailored soil mix, ensuring optimal conditions for their plants and improving drainage.
- Reduced Pests and Weeds: Elevating the garden limits the spread of weeds and can deter some pests from accessing your plants.
- Extended Growing Season: The soil in raised beds warms up faster in the spring, allowing for earlier planting and longer harvest seasons.
Design and Aesthetics
Choosing the Right Size for Your Space
One of the first steps when considering landguard raised beds is to determine the appropriate size for your garden space. A standard width of 4 feet and length dependent on available space often allows for efficient planting and maintenance. Here are some guidelines to help in your decision:
- Small Spaces: For limited spaces like balconies or patios, smaller beds measuring 2×4 feet or even square options are ideal.
- Medium to Large Yards: For expansive areas, consider beds that are 4×8 feet or larger, allowing for diverse planting options.
- Height Considerations: Standard heights range from 1 to 3 feet. A taller bed is easier to garden without bending, but ensure it fits aesthetically within your landscape.
Color and Material Options
The aesthetic choices of landguard raised beds can significantly impact the overall look of your garden. Common material choices include:
- Galvanized Steel: Highly durable and resistant to rust, these beds are available in various colors, often offering a modern or industrial aesthetic.
- Wood: Wooden beds provide a natural look and can be painted or stained to match your garden theme, but ensure they are treated to resist decay.
- Composite Materials: Some beds utilize recycled materials, combining durability with a wood-like appearance for an eco-friendly choice.
Integrating Landguard Raised Beds into Your Landscape Design
Successfully incorporating raised beds into your landscaping flows from planning and design. Here are strategies to seamlessly integrate these beds:
- Placement: Position raised beds in locations that receive ample sunlight, ideally receiving at least 6-8 hours of direct light each day.
- Grouping: Consider placing several beds together to create a cohesive garden area, which can foster a vibrant community of plants and enhance visual appeal.
- Surrounding Landscape: Introduction of pathways, seating areas, or ornamental plants around the raised beds can enhance usability and enjoyment while aiding accessibility.
Installation and Setup
Step-by-Step Installation Process
Setting up landguard raised beds is a straightforward process that can be accomplished in just a few steps:
- Select a Location: Choose a level area with adequate sunlight and easy access to water.
- Prepare the Ground: Clear the area of debris, grass, and weeds to create a clean base.
- Assemble the Bed: Following manufacturer instructions, usually requiring basic tools like a screwdriver and wrench, connect the components to form the bed.
- Level the Bed: Ensure the bed is level for proper drainage and overall stability.
- Add Soil: Fill the bed with a suitable soil mix tailored for the crops you plan to grow.
Essential Tools for Setup
Having the right tools will make installing landguard raised beds a breeze. Here’s a list of essentials:
- Screwdriver or Drill
- Wrench
- Level
- Shovel or trowel for soil placement
- Soil or compost for filling
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Installation
While the process is generally simple, avoid common pitfalls to maximize your results:
- Improper Sizing: Ensure the bed size suits your gardening needs and space.
- Neglecting Drainage: Proper drainage is crucial. Avoid placing raised beds in low-lying areas that do not drain well.
- Ignoring Soil Quality: Use high-quality soil blends suitable for the crops to ensure optimal growth.
Planting and Maintenance Tips
Best Soil Mixes for Landguard Raised Beds
The success of a garden largely depends on soil quality. Here are recommended soil mixes for landguard raised beds:
- Layered Approach: Combine equal parts of organic compost, peat moss, and vermiculite or perlite for excellent drainage and nutrient retention.
- Specific Crop Needs: Adjust the soil mix based on the plants being grown. For instance, root vegetables may require denser soil, while leafy greens thrive in lighter mixes.
Watering and Fertilizing Best Practices
Maintaining proper hydration and nutrition is essential for thriving plants. Here are best practices to follow:
- Consistent Watering: Raised beds often dry out more quickly. Water regularly, ensuring moisture reaches the root zone without waterlogging.
- Organic Fertilizers: Incorporate organic fertilizers or compost every 4-6 weeks, adjusting based on plant species and growth stages.
Pest Control Strategies for Raised Beds
Preventing pests is crucial for sustaining plant health in raised beds. Effective strategies include:
- Physical Barriers: Use nets or row covers to keep pests away from delicate plants.
- Companion Planting: Strategically plant certain species together to deter insects and enhance growth.
- Natural Pesticides: Employ organic solutions like neem oil or insecticidal soap to target pests without harming beneficial insects.
Maximizing Harvest with Landguard Raised Beds
Choosing the Right Crops for Your Raised Beds
The crops you select can significantly impact the yield from landguard raised beds. Here are ideal crop choices:
- Vegetables: Tomatoes, peppers, lettuce, and carrots thrive in raised beds.
- Herbs: Basil, parsley, and cilantro flourish in limited space, providing flavors for a variety of dishes.
- Flowers: Marigolds and nasturtiums also do well, adding beauty to the gardening space while attracting beneficial insects.
Seasonal Planting Guidelines
Seasonal planting maximizes the productivity of your garden. Follow these guidelines:
- Spring Planting: Early spring is ideal for cool-weather crops like peas and spinach, which can be sown as soon as the soil is workable.
- Summer Planting: As the season warms, plant heat-loving crops such as cucumbers, eggplants, and peppers.
- Fall and Winter Prep: Consider planting cover crops in the fall to improve soil health and prevent erosion during the winter months.
Harvesting Techniques for Optimal Yield
To achieve the best possible yield from your landguard raised beds, employ these harvesting techniques:
- Timing: Harvest crops at their peak ripeness for optimal flavor and nutritional value.
- Gentle Handling: Use proper techniques to prevent damaging plants or reducing yields by incorrect cutting methods.
- Regular Check-ups: Monitor your plants frequently to ensure you can harvest promptly and take corrective measures if needed.