Introduction to Modular Belt Technology
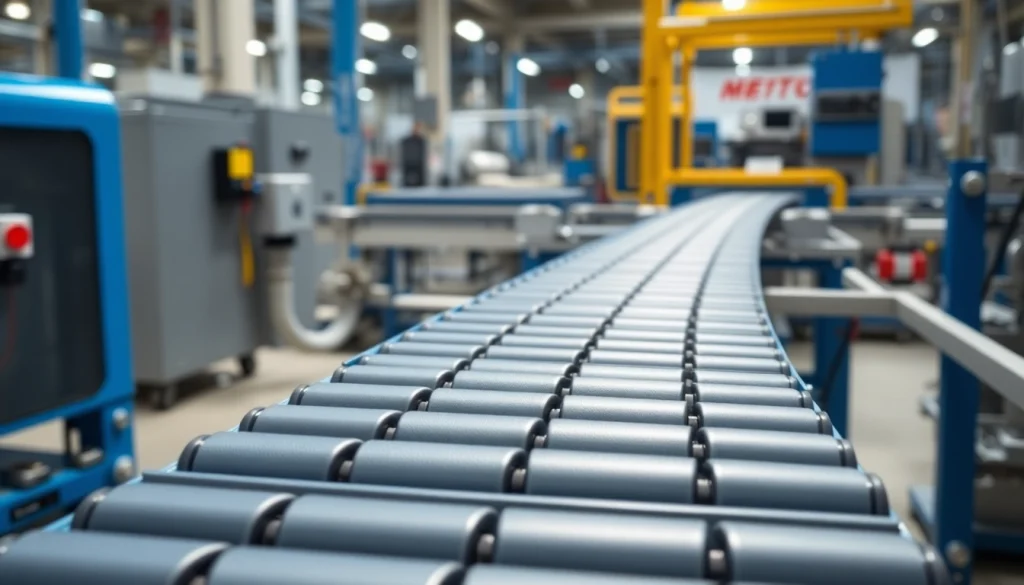
In the world of conveyor systems, modular belts have emerged as a versatile and efficient solution to material handling challenges across various industries. These belts, which are made of interlocking plastic segments, offer a range of advantages that cater to different operational needs. Understanding the structure, materials, and applications of modular belts can lead to better decisions for businesses looking to enhance their conveying systems.
Defining Modular Belts and Their Structures
Modular belts are intricately designed conveyor belts consisting of individual modules that are linked together. Each module is typically rectangular and features a series of grooves or tabs that help align the segments, ensuring smooth movement along the conveyor. This unique design allows for flexibility and adaptability, making modular belts suitable for a variety of applications, from food processing to automotive assembly lines.
Materials Used in Modular Belts
Manufacturers often use various types of plastic in the production of modular belts, such as polypropylene, polyethylene, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). These materials are chosen for their durability, resistance to chemicals, and ability to withstand diverse temperature ranges. For instance, some modular belts can operate effectively in environments featuring extreme temperatures, while others are designed to resist the corrosive effects of cleaning agents commonly used in food processing areas.
Common Applications of Modular Belts
Modular belts are used in numerous industries due to their adaptability. Some of the most common applications include:
- Food and Beverage Industry: Modular belts provide efficient movement of products and components, enabling high hygiene standards.
- Automotive Manufacturing: The belts support heavy loads and complex routes, essential for assembly line efficiency.
- Packaging and Distribution: Modular systems can easily integrate into existing conveyor setups to facilitate product movement during packaging and distribution.
- Pharmaceuticals: They adhere to strict hygiene regulations while offering durability and compliance with industry standards.
Advantages of Using Modular Belts
Increased Durability and Maintenance Ease
One of the key advantages of modular belts is their durability. They can tolerate rigorous operating conditions and resist wear and tear better than some traditional belt systems. When sections wear out, they can be easily replaced without needing to replace the entire belt, significantly reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Adaptability to Various Industries
The modular design allows for customization in size, shape, and material, making these belts adaptable to a wide range of industries. They can handle diverse products, whether they are lightweight items in the packaging industry or heavy components in manufacturing, thereby improving efficiency across different sectors.
Cost-Effectiveness Over Time
While the initial investment in modular belts may be higher compared to other conveyor systems, they offer long-term cost savings. Their durability and ease of maintenance result in lower overall operating costs. Additionally, their modularity allows for scalability as business needs evolve, reducing the need for complete system overhauls.
Choosing the Right Modular Belt for Your Needs
Understanding Load Capacities and Specifications
When selecting a modular belt, understanding the load capacity is crucial. Each type of belt is engineered to handle specific weight ranges and product types. It’s important to consider the weight, size, and stability of the products being conveyed to choose the appropriate belt that ensures efficient operation without strain or failure.
Factors to Consider in Design Selection
Several factors play a pivotal role in designing a modular belt system:
- Width and Length: Depending on the application, the required width and length of the belt should be assessed to ensure it fits the conveyor system.
- Surface Texture: The surface of the belt can impact product movement. A textured surface may be necessary for items that require extra grip.
- Temperature Tolerance: In environments where heat or cold is a factor, select belts that can function optimally within those temperature ranges.
Custom Solutions for Unique Applications
Custom solutions can be engineered for unique applications. Collaborating with manufacturers allows businesses to design belts that meet specific requirements, such as shapes to fit unique conveyor configurations or specialized surfaces for different products. This customization enhances efficiency and can significantly improve product handling.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Step-by-Step Installation Process
The installation of a modular belt system involves several key steps:
- Preparation: Ensure the conveyor frame is clean and free of debris. Gather all necessary tools and replacement parts.
- Module Arrangement: Arrange the modules on a flat surface to ensure a proper fit. This includes checking for alignment and compatibility.
- Assembly: Connect the modules according to the manufacturer’s instructions, using the appropriate connecting pins and fittings.
- Tensioning: Adjust the tension as needed to ensure smooth operation without slippage or excessive friction.
- Testing: Conduct a test run to check for proper functionality and make any necessary adjustments before the full operation.
Regular Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Routine maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity of modular belts. Here are some practices to follow:
- Regularly check for signs of wear and replace damaged sections promptly.
- Clean the belts periodically to remove debris and prevent buildup that can affect performance.
- Monitor tension and alignment to ensure smooth operation and prevent unnecessary strain.
- Keep an eye on the drive system for signs of failure which could impact belt operation.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Techniques
Even with excellent maintenance, issues can arise with modular belts. Common problems include:
- Slippage: Can be caused by insufficient tension. Adjust the tension to remedy this issue.
- Wear and Tear: Inspect the belt regularly; replace worn parts to prevent further damage.
- Misalignment: Check the alignment regularly to avoid uneven wear or functioning; make adjustments accordingly.
The Future of Modular Belts in Industries
Innovative Technologies Shaping Modular Design
Technological advancements continue to shape the evolution of modular belts. Innovations include smart technology that tracks performance metrics, automating maintenance checks, and improving overall system efficiency. The integration of IoT devices allows for real-time monitoring and enhances predictive maintenance capabilities, reducing downtime.
Sustainability Trends in Conveyor Systems
The push for sustainability is influencing modular belt design as manufacturers seek to create eco-friendly products. Biodegradable materials, energy-efficient operation, and designs that reduce waste are now essential considerations in the production of modern modular belts. This trend not only helps meet regulatory demands but also aligns with corporate responsibility goals.
Market Growth and Emerging Applications
As industries continue to evolve, the market for modular belts is expected to grow. New applications are emerging, particularly in sectors such as e-commerce, where rapid fulfillment requires efficient and flexible conveyor systems. As businesses embrace automation, modular belts will play a critical role in streamlining operations and optimizing supply chains.